Everything You Need to Know About Your First Electrocardiogram Session
2021-08-12
No other chronic health condition has plagued and claimed as many American lives as heart disease. As the leading cause of death in the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states that one person dies of cardiovascular complications every 36 seconds.
Despite this startling data, the CDC also shares that 80% of cardiovascular diseases are preventable with early intervention. Considering that most heart attacks manifest symptoms weeks ahead, many healthcare professionals rely on tests for early detection — the electrocardiogram is one of them.
What is an electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a straightforward test that measures your heart’s electrical activity. It is also painless, non-invasive, and can be completed relatively quickly. More often than not, an ECG only takes about 10 minutes in a physician office.
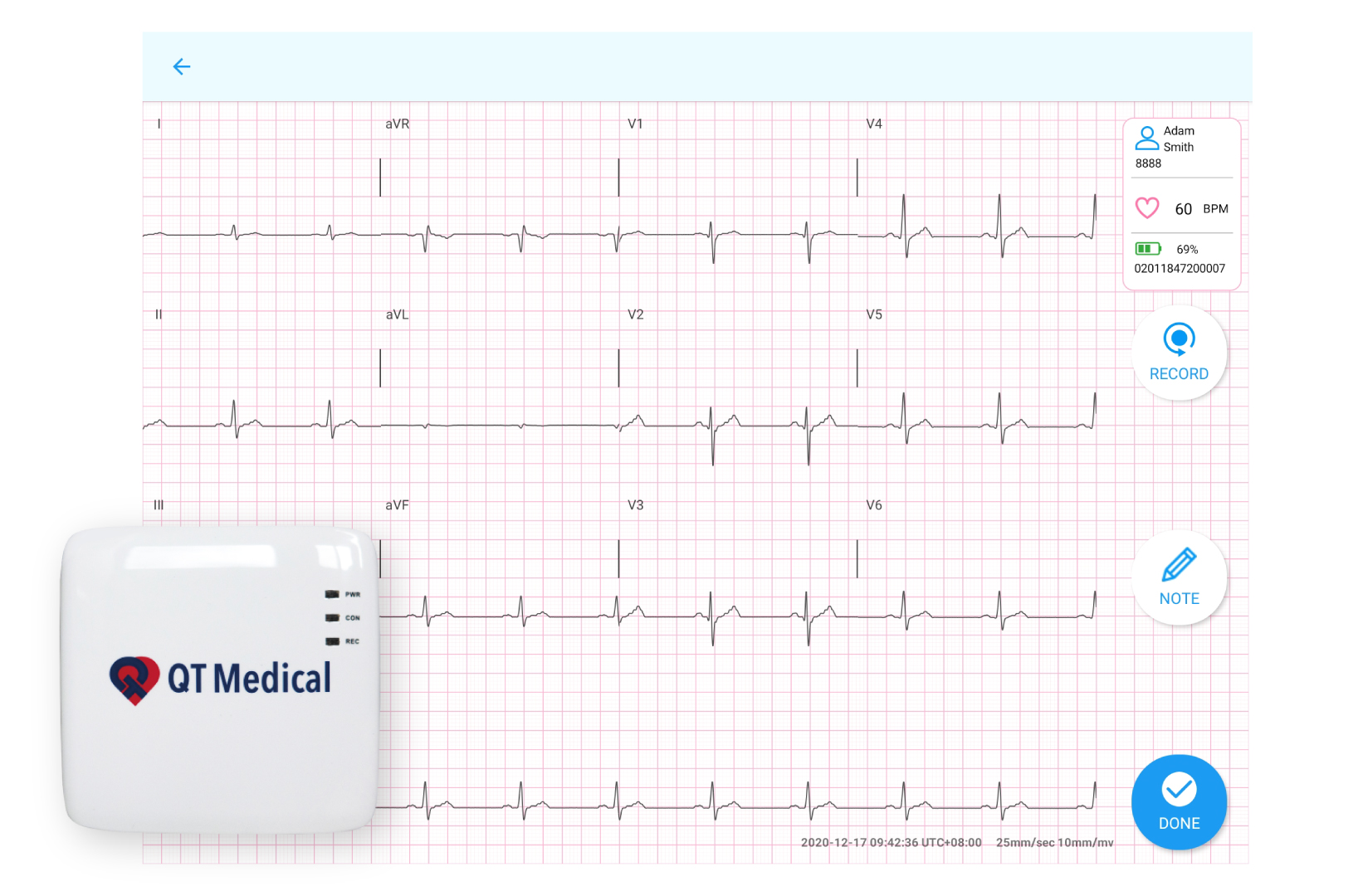
The ECG machine is composed of electrodes (small patches) that have a light non-irritating adhesive quality. These are attached to specific parts of the body, namely the chest, arms, and legs, since these areas are most conducive for the procedure. These electrodes then use lead wires to connect them to the ECG machine.
There are various types of ECGs a medical expert may request. The most common ones are the resting ECG, the stress test, the Holter monitor, and event recorders.
What are they used for?
The heart sends out natural electrical impulses with every contraction to keep blood flowing. With an ECG, your heart’s electrical activity can be accurately recorded, measured, and presented for a healthcare worker’s analysis.
When would I need an electrocardiogram?
Depending on your medical history, a medical expert may suggest an ECG to determine the wellbeing of your heart. Healthcare staff may request this test if a patient exhibits chest pains, irregular heartbeats, unusual chest sounds, dizziness, shortness of breath, and severe exhaustion.
An ECG can also check on the state of a pacemaker and monitor the heart before and after invasive procedures. Because ECGs provide a comprehensive look into the wellbeing of this major organ, even perfectly healthy patients can be given an ECG during general physical exams.
What are the risks of an electrocardiogram?
Generally, there are no real risks related to ECG testing. If any, these are very rare, with minimal skin irritations due to the placement of the electrodes. In the event of contact dermatitis, patients can relieve symptoms with hydrocortisone cream. It must be noted, though, that there have been some cases of supposedly clean wires testing positive for antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Hence, as an added precautionary step, PCA 500 eliminates the threat of contaminated wires with a system that is easier to clean and store.
What to expect during an electrocardiogram
During the procedure, you will be asked to remove or lift your clothes to apply the electrodes. In some cases, patients will be provided a medical gown. Any accessories that may get in the way like bracelets or necklaces should also be removed. For patients with more body hair, you may be asked to shave to eliminate interference between the ECG components and your skin. Depending on the ECG test, the professional overseeing your test may ask you to lie down, sit up, or run.
What do the results mean?
For most people, the results of any ECG look like nothing more than peaks and dips. However, in the trained hands of a professional, these illustrate the state of a patient’s heart. By translating these readings, healthcare workers can see if you have any blockages, irregularities, or other concerns.
Primary physicians will typically use these readings to inform your next step in the treatment. This can help them determine whether you need medication, treatment, or any other lifestyle changes. Though in the event that a primary physician isn't present, nurses who’ve completed their post-master’s nurse certification are also competent at handling and analyzing ECG test results. These post-graduate studies enable registered nurses to further their expertise, which includes analyzing ECG tests. Considering that the field of adult-gerontology is booming as more patients near retirement age, nurse practitioners are expected to use their capabilities to address this demand, and can help adults and even children understand if their hearts are beating normally or at an abnormal pace. Abnormalities may point to heart damage or heart disease and may need further consultation with heart specialists.
What happens after an electrocardiogram?
Typically, there is no special after-care needed following an ECG. If you’ve had a stress test or if you were already exhibiting symptoms before the test, your healthcare provider may ask you to look out for nausea, chest pains, or difficulty breathing. Otherwise, most recommendations will more likely be about proper exercise and healthy dietary adjustments. Foods like asparagus, coffee, and green tea can help maintain a healthy heart.
If you’ve never experienced it, an ECG may seem like a frightening test. However, with the guidance of a professional, a positive attitude, and a calm mind, this simple procedure can help improve your overall quality of life.
Post specially written for qtmedical.com
Post by: JBundy
FAQ
What is a medical ECG?
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple, non-invasive, and painless test that records the electrical activity in your heart. ECGs are used to check for signs of heart disease.
What is the difference between a single lead (1-lead) and a 12-lead ECG?
A single-lead ECG is used for arrhythmia detection and basic heart monitoring. A 12-lead ECG is used to provide a comprehensive view of the heart and is the medical standard for screening and diagnosing various heart conditions. A 12-lead ECG is often used to detect or diagnose arrhythmias, heart attacks, drug effects on the heart, and many other heart diseases.
What happens during an ECG?
During an ECG, up to 12 sensors (electrodes) will be attached to your chest and limbs. The electrodes are sticky patches with wires that connect to a monitor. They record the electrical signals that make your heart beat. A computer records the information and displays it as waves on a monitor or on paper.
You can breathe normally during the test, but you will need to lie still. Make sure you're warm and ready to lie still. Moving, talking or shivering may distort the test results. A standard ECG takes a few minutes.
Is ECG test painful?
No. There’s no pain or risk associated with having an electrocardiogram. When the ECG stickers are removed, there may be some minor discomfort.
Can ECG be done at home?
PCA 500 is user-friendly and easy to apply. It can be used by patients themselves. For females, it is recommended to lie flat for the test. Therefore, for females and elderly patients, it is advised to have a trusted one to help.
See more patients FAQ